We present a detailed study of the charge transport characteristics of double-stranded DNA oligomers including the oxidative damage 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG). The problem is treated by a hybrid methodology combining classical molecular dynamics simulations and semiempirical electronic structure calculations to formulate a coarse-grained charge transport model. The influence of solvent- and DNA-mediated structural fluctuations is encoded in the obtained time series of the electronic charge transfer parameters. Within the Landauer approach to charge transport, we perform a detailed analysis of the conductance and current time series obtained by sampling the electronic structure along the molecular dynamics trajectory, and find that the inclusion of 8-oxoG damages into the DNA sequence can induce a change in the electrical response of the system. However, solvent-induced fluctuations tend to mask the effect, so that a detection of such sequence modifications via electrical transport measurements in a liquid environment seems to be difficult to achieve.
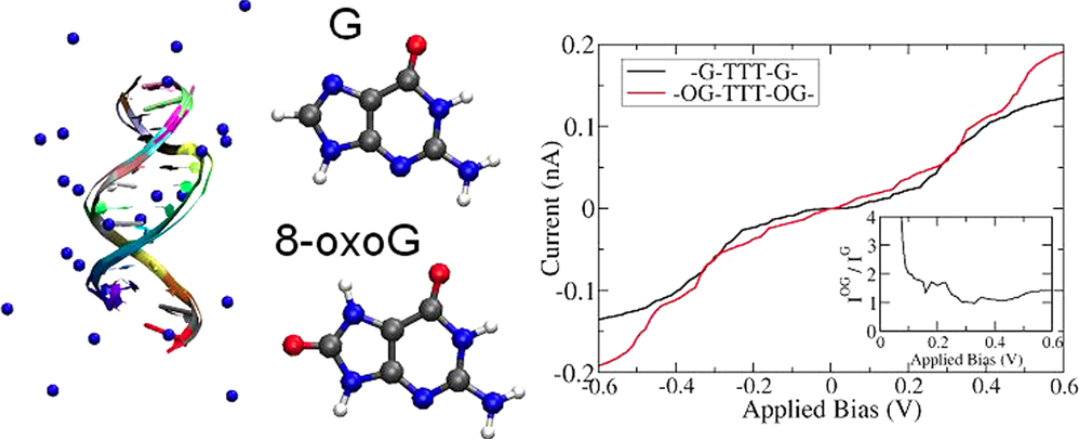
We present a detailed study of the charge transport characteristics of double-stranded DNA oligomers including the oxidative damage 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG). The problem is treated by a hybrid methodology combining classical molecular dynamics simulations and semiempirical electronic structure calculations to formulate a coarse-grained charge transport model. The influence of solvent- and DNA-mediated structural fluctuations is encoded in the obtained time series of the electronic charge transfer parameters. Within the Landauer approach to charge transport, we perform a detailed analysis of the conductance and current time series obtained by sampling the electronic structure along the molecular dynamics trajectory, and find that the inclusion of 8-oxoG damages into the DNA sequence can induce a change in the electrical response of the system. However, solvent-induced fluctuations tend to mask the effect, so that a detection of such sequence modifications via electrical transport measurements in a liquid environment seems to be difficult to achieve.
