ZnO in its many forms, such as bulk, thin films, nanorods, nanobelts, and quantum dots, attracts significant attention because of its exciting optical, electronic, and magnetic properties. For very thin ZnO films, predictions were made that the bulk wurtzite ZnO structure would transit to a layered graphene-like structure. Graphene-like ZnO layers were later confirmed when supported over a metal substrate. However, the existence of free-standing graphene-like ZnO has, to the best of our knowledge, not been demonstrated. In this work, we show experimental evidence for the in situ formation of free-standing graphene-like ZnO mono- and bilayer ZnO membranes suspended in graphene pores. Local electron energy loss spectroscopy confirms the membranes comprise only Zn and O. Image simulations and supporting analysis confirm that the membranes are graphene-like ZnO. Graphene-like ZnO layers are predicted to have a wide band gap and different and exciting properties as compared to other ZnO structures.
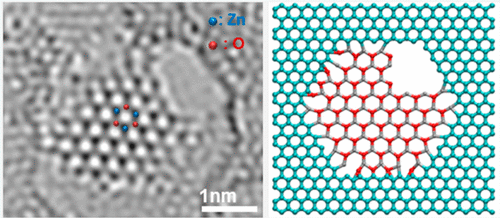
ZnO in its many forms, such as bulk, thin films, nanorods, nanobelts, and quantum dots, attracts significant attention because of its exciting optical, electronic, and magnetic properties. For very thin ZnO films, predictions were made that the bulk wurtzite ZnO structure would transit to a layered graphene-like structure. Graphene-like ZnO layers were later confirmed when supported over a metal substrate. However, the existence of free-standing graphene-like ZnO has, to the best of our knowledge, not been demonstrated. In this work, we show experimental evidence for the in situ formation of free-standing graphene-like ZnO mono- and bilayer ZnO membranes suspended in graphene pores. Local electron energy loss spectroscopy confirms the membranes comprise only Zn and O. Image simulations and supporting analysis confirm that the membranes are graphene-like ZnO. Graphene-like ZnO layers are predicted to have a wide band gap and different and exciting properties as compared to other ZnO structures.
